| Quantum Channel Decoding |
| Using NISQ quantum computers for channel decoding |




|
Channel Coding is the technique that enables reliable delivery of digital data over unreliable communication
channels. For most high performance channel coding techniques, the existing classical algorithms are computationally
expensive, making them impractical for throughput-demanding applications with large code sizes. Today's Noisy
Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) computers, although limited due to a modest number of qubits, short coherence time,
and poor gate fidelity, are useful tools for exploring and experimenting with possible solutions to a wide variety of
computational problems.
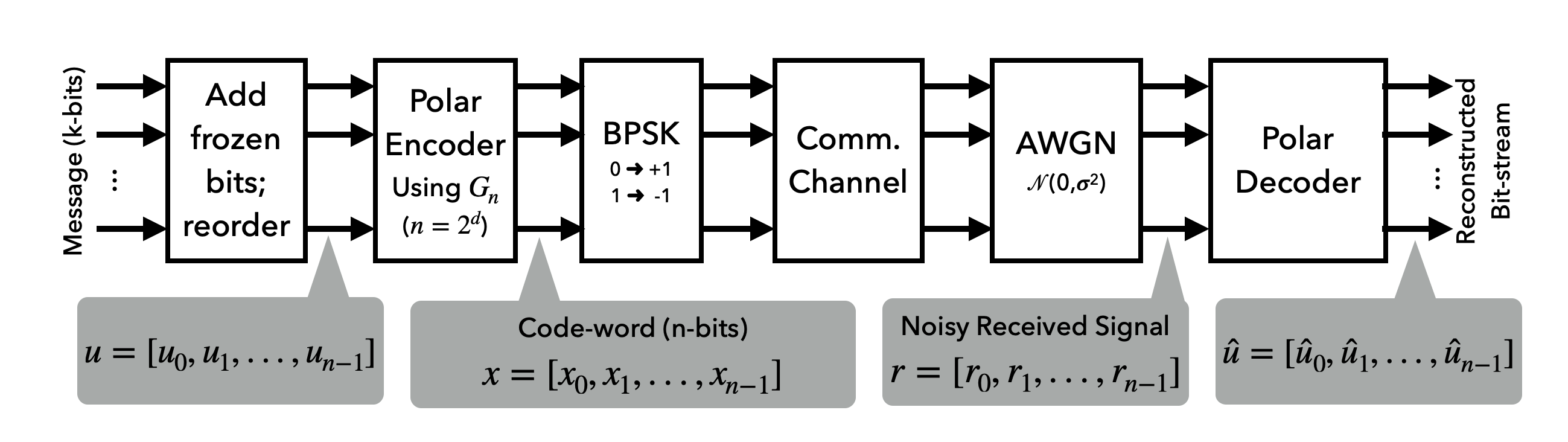
In this research, we showed how careful initialization of qubits combined with a simple quantum circuit, enables us to perform
channel decoding for different linear block codes. We first described our novel qubit initialization technique which we call
"Quantum Soft Decision" and then designed a simple quantum circuit—"Quantum Generator"—based on the Generator
or Parity-check matrix. Using these universal concepts, we implemented Quantum Decoders for two different types of linear
block codes, namely Hamming codes and Polar codes.
For more details, please refer to our paper which was presented in
IEEE QCE 2022 conference.
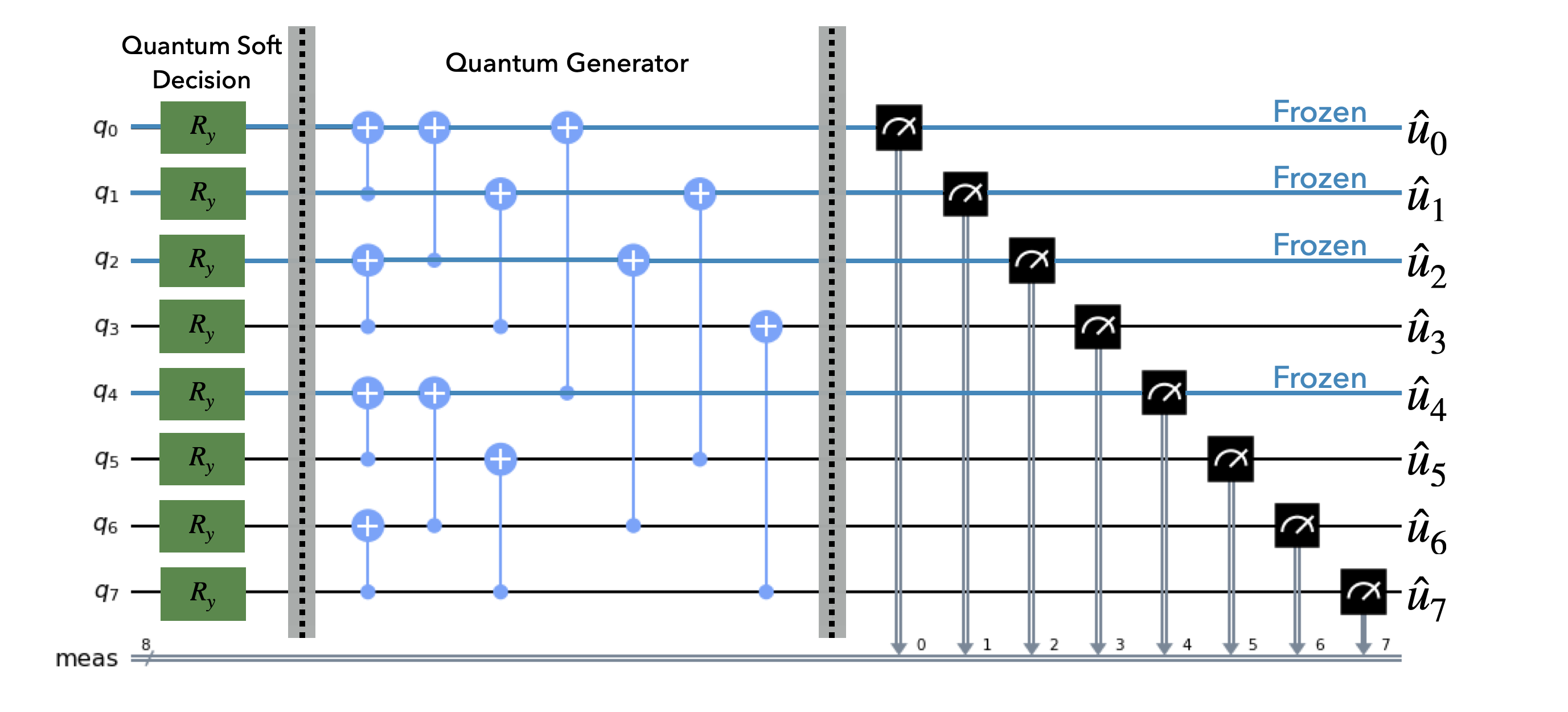
Here is an example of quantum circuit for an (8,4) Polar Code:
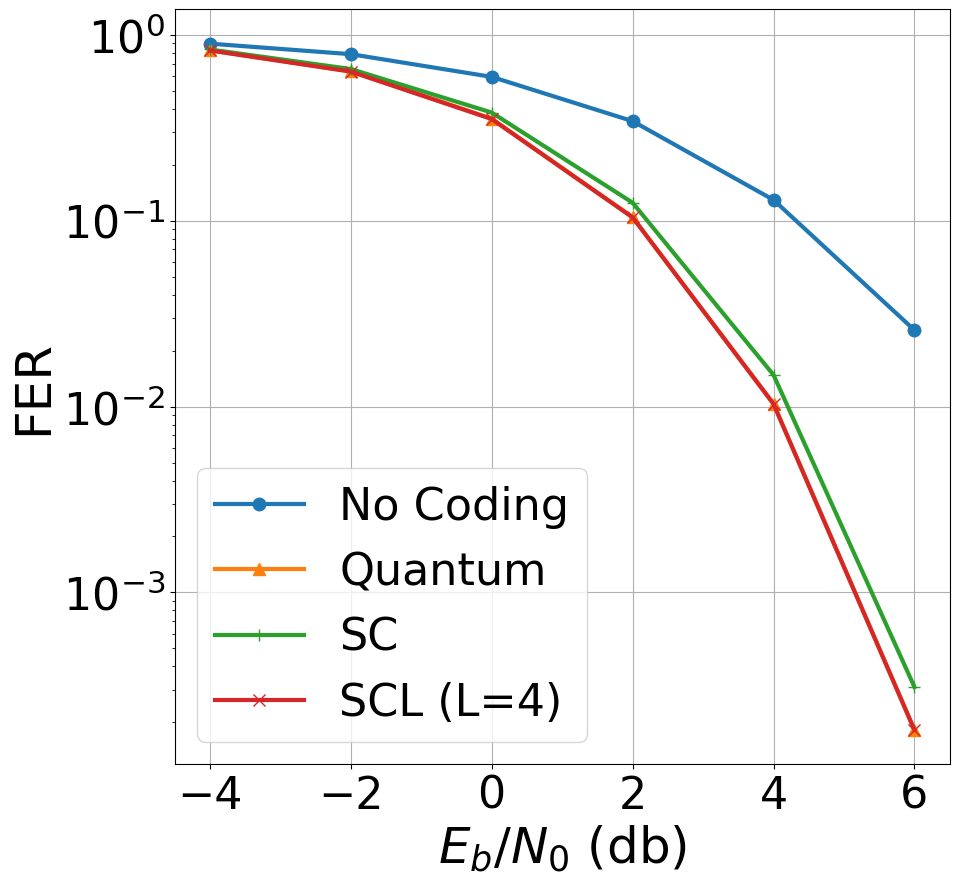
The following diagram compares the Frame Error Rate (FER) at different Eb/N0 ratios for a (16,11) Polar code with Successive Cancellation (SC), Successive Cancellation
List (SCL), and Quantum decoding. As it can be seen, the performance of Quantum Decoder matches SCL—one of the best
classical algorithm for Polar codes.
The following video briefly explains this research. It was prepared for the IEEE QCE 2022 conference.